In the world of display technology, two main screen types are often discussed: segmented LCD (liquid crystal display) and TFT (thin film transistor) displays. Both technologies have their own unique characteristics, advantages, and applications. Understanding the difference between segmented LCD and TFT can help consumers and manufacturers make an informed decision based on their respective needs.
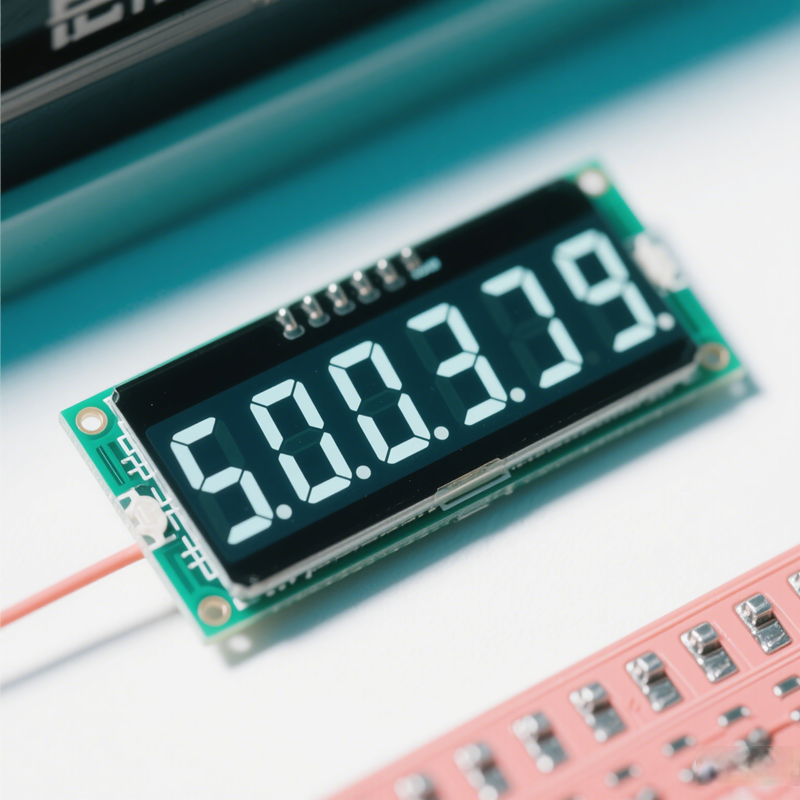
What is Segment LCD?
Segment LCDs are a type of display technology that utilizes liquid crystals to create images. They are primarily used for displaying numerical data and simple graphics. Segment LCDs consist of a series of segments that can be turned on or off to form characters or symbols. The most common example of segment LCDs is the digital clock or calculator display, where numbers are formed by illuminating specific segments.
Segment LCDs are typically monochrome, meaning they display images in a single color, usually black on a light background or vice versa. They are known for their low power consumption, making them ideal for battery-operated devices. The simplicity of segment LCDs allows for easy readability, even in bright lighting conditions.
What is TFT?
TFT, or Thin Film Transistor, is a more advanced display technology that is widely used in modern screens, including smartphones, tablets, and televisions. TFT displays are a type of active matrix LCD, which means they use a grid of transistors to control individual pixels. This allows for a much higher resolution and more vibrant colors compared to segment LCDs.
TFT displays can produce full-color images and are capable of displaying complex graphics and videos. They offer better viewing angles, faster response times, and improved contrast ratios. The technology behind TFT allows for a more dynamic and visually appealing user experience, making it the preferred choice for applications that require high-quality visuals.
Key Differences Between Segment LCD and TFT
Display Type:
Segment LCD: Primarily used for displaying simple characters and symbols. It is limited to a fixed number of segments, which restricts its ability to show complex images.
TFT: Capable of displaying full-color images and videos. It can produce millions of colors and is suitable for a wide range of applications, from simple user interfaces to high-definition video playback.
Resolution:
Segment LCD: Generally has a low resolution, as it is designed for basic displays. The resolution is often limited to a few digits or simple graphics.
TFT: Offers high resolution, allowing for detailed images and text. This makes TFT displays ideal for applications that require clarity and precision.
Color Capability:
Segment LCD: Typically monochrome, with limited color options. Some segment LCDs may offer dual-color displays, but they are still far from the color richness of TFT.
TFT: Supports full-color displays, with the ability to show a wide spectrum of colors. This makes TFT displays suitable for multimedia applications.
Power Consumption:
Segment LCD: Known for low power consumption, making it ideal for battery-operated devices. The simplicity of the technology allows for extended battery life.
TFT: Generally consumes more power than segment LCDs, especially when displaying bright images or videos. However, advancements in technology have led to more energy-efficient TFT displays.
Cost:
Segment LCD: Typically less expensive to produce, making them a cost-effective choice for simple applications. They are often found in low-cost devices.
TFT: More expensive due to the complexity of the technology and the higher quality of the display. This cost is justified in applications where high-quality visuals are essential.
Applications:
Segment LCD: Commonly used in devices like calculators, digital watches, and simple appliances where basic information display is sufficient.
TFT: Found in smartphones, tablets, laptops, and televisions, where high-quality graphics and video playback are necessary.
Conclusion
In summary, segment LCDs and TFT displays are designed for different applications and functions. Segment LCDs are best suited for simple, low-power displays with limited information, while TFT displays are better at presenting high-quality images and complex graphics. When choosing between the two, it is important to evaluate the specific needs of the application, such as resolution, color options, power consumption, and budget. Understanding these differences can help consumers and manufacturers choose the right display technology to ensure better performance and user satisfaction.
Post time: Apr-21-2025

